Introduction: Understanding Isometric Drawing Paper
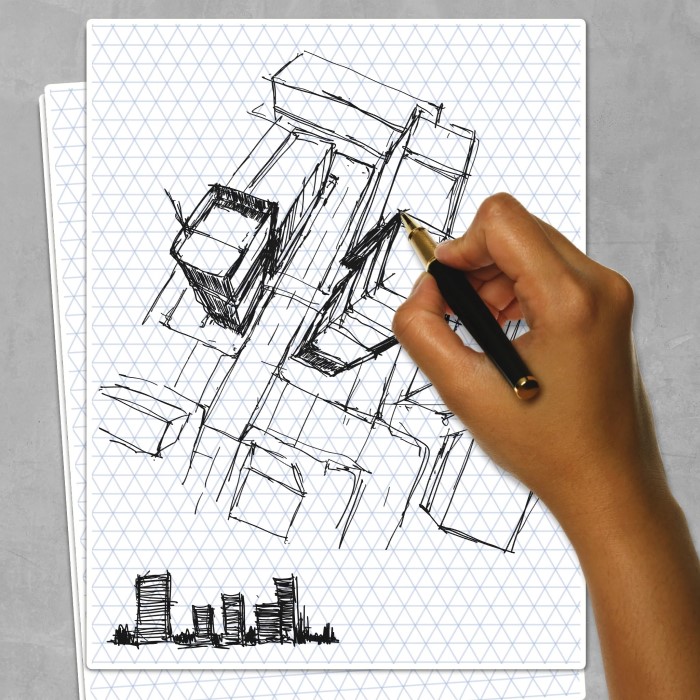
Isometric drawing paper plays a crucial role in the world of technical drawing. With its unique grid system, it allows artists and designers to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface. Isometric drawing paper features a network of equilateral triangles that helps create depth and perspective in artwork, making it an indispensable tool for various fields, including architecture, engineering, and gaming design. In this detailed guide, we will explore the characteristics of isometric drawing paper, its benefits, uses, and best practices for effectively employing it in your creative projects.

The Concept of Isometric Drawing
What is Isometric Drawing?
Isometric drawing is a method of depicting three-dimensional objects in two dimensions, where the dimensions along each axis are scaled evenly. This means that measurements are proportionate, allowing artists and designers to maintain accuracy and clarity in their illustrations.
- Equal Scaling: Unlike perspective drawing, isometric drawings don’t employ vanishing points, resulting in a more straightforward interpretation of dimensions. All angles remain constant at 120 degrees, which prevents distortion.
- Practical Applications: Isometric drawings are widely used in disciplines such as engineering and architecture, enabling professionals to depict plans, diagrams, and technical schematics.
The Role of Isometric Drawing Paper
Isometric drawing paper is specifically designed to aid in the creation of these kinds of drawings. Its grid of equilateral triangles makes it easier to create shapes that are proportionate and visually accurate.
- Grid Layout: The triangular grid forms an underlying structure that artists use to guide their drawing, ensuring accurate representations of objects.
- Useful for All Skill Levels: Whether you’re a novice or an experienced designer, isometric drawing paper simplifies the drawing process. The pre-printed grids provide visual support, helping users free themselves from errors arising from manual measurement.
Benefits of Using Isometric Drawing Paper
1. Precision and Clarity
One of the primary advantages of using isometric drawing paper is its ability to enhance precision:
Proportional Drawings
- Facilitating Proportions: Each section of the triangular grid aids artists in creating shapes that are proportionate and well-balanced. By offering a clear framework, the grid ensures that all elements of the drawing relate harmoniously to one another.
- Accurate Representation of Lines and Angles: The triangular grid provides precise guidelines for representing lines and angles, making it an essential tool for technical drawings. This accuracy is crucial in fields such as architecture, engineering, and industrial design, where exact measurements are necessary.
- Versatility in Design: Artists can utilize the grid to create a variety of shapes, from simple geometric forms to complex structures. This versatility makes it easier to experiment with different shapes and designs while maintaining proportionality.
- Enhancing Technical Skills: Proportional drawings using a triangular grid can help artists develop their technical skills. By practicing within the constraints of the grid, artists learn to understand and apply principles of proportion and scale effectively.
- Streamlining the Design Process: With a structured grid to guide their drawings, artists can navigate the design process more efficiently. This structured approach can result in quicker iterations, allowing for more time to focus on creative aspects.
Reduction of Errors
- Minimizing Mistakes: The organized nature of the triangular grid significantly reduces drawing errors. By providing a clear visual reference, artists can avoid common pitfalls, such as misaligned lines and incorrect angles.
- Fostering Confidence in Execution: With the grid acting as a reliable guide, artists can be more confident in their technical execution. This increased confidence can lead to improved overall quality in their work.
- Emphasis on Aesthetics and Creativity: With less worry about dimensions and proportional accuracy, artists can dedicate their mental energy to exploring aesthetics and creative ideas. This focus on artistic expression allows for more innovative designs.
- Encouraging Experimentation: The grid’s structured layout allows artists to experiment with various styles and concepts without the fear of making critical errors. Artists can freely explore their creativity within the constraints of the grid while maintaining accuracy.
- Improving Workflow Efficiency: By minimizing the need for revisions due to drawing errors, artists can enhance their workflow efficiency. A more streamlined process can lead to greater productivity and the ability to take on more projects or complex designs.
2. Simplification of Complex Designs
Isometric drawing paper minimizes the complexity involved in creating intricate designs:
- Quick Visualization: With a clear and structured grid, designers can quickly visualize relationships among various elements, laying the groundwork for their projects.
- Streamlined Workflow: This simplification allows for efficient project planning, ultimately saving time while maintaining high-quality results.
Common Uses of Isometric Drawing Paper
1. Architectural and Engineering Drawings
Isometric drawing paper is invaluable in the architectural and engineering sectors:
Blueprint Creation
- Visual Communication: Architects utilize isometric drawings as a vital tool for conveying design concepts to clients. These drawings provide a three-dimensional representation on a two-dimensional plane, making concepts easier to understand.
- Engaging Design Representation: Isometric drawings enhance the aesthetic appeal of architectural presentations. The use of angles and proportions creates a visually engaging layout that captures clients’ attention and showcases the architectural vision effectively.
- Illustrating Complex Structures: Architects can use isometric drawings to illustrate a wide range of buildings and landscapes, from residential homes to large commercial spaces. This versatility enables them to convey ideas across various project types.
- Maintaining Proportion and Scale: One of the key benefits of isometric drawing is its ability to maintain accurate proportions and scales. By using a consistent angle, architects can ensure that all elements of the design relate to one another in a realistic manner, helping clients visualize the final outcome.
- Facilitating Client Understanding: By presenting ideas in a clear and engaging way, isometric drawings can help bridge communication gaps between architects and clients. Clients are more likely to comprehend design intentions, leading to more informed feedback and decisions.
Mechanical Designs
- Precision in Engineering: Engineers rely heavily on isometric drawings for drafting mechanical components. These drawings allow for a clear representation of complex parts and assemblies, which is crucial for engineering accuracy.
- Utilizing a Grid System: The grid structure inherent in isometric drawings provides a framework for engineers to depict mechanical components precisely. This grid system helps ensure that every component is accurately scaled and positioned relative to others.
- Ensuring Proper Fits: In mechanical design, ensuring that parts fit together correctly is critical. Isometric drawings allow engineers to visualize assemblies and check for potential interference or misalignment before physical production begins.
- Clarifying Complex Assemblies: For intricate mechanical systems with many components, isometric drawings help clarify how pieces interact or fit together. This visual clarity can be essential for troubleshooting design issues or for communicating assembly instructions to team members.
- Documenting Specifications: Isometric drawings not only guide manufacturing but also serve as documentation for mechanical designs. Engineers can annotate these drawings with key specifications, measurements, and materials, creating a comprehensive reference for production and assembly teams.
2. Game Design and Animation
The gaming and animation industries also benefit from isometric drawing techniques:
- Level Design: Game designers utilize isometric drawing to plan and visualize levels, ensuring smooth gameplay experiences by accounting for spatial relationships.
- Character Modeling: Animators can represent characters and objects using isometric drawing paper, allowing them to maintain consistent proportions when creating animations.
Techniques for Drawing on Isometric Paper
1. Using the Right Tools
While isometric drawing paper provides a fantastic base for creativity, the right tools can enhance your work:
- Drafting Tools: Utilize drafting tools like rulers, set squares, and compasses to enable precision in your lines and angles. A good quality pencil or fineliner can introduce sharpness and clarity into your illustrations.
- Colored Pencils and Markers: Adding color enhances the visual appeal of your drawings. You can use colored pencils or markers to differentiate between various elements in your design.
2. Practice Regularly
Engaging with isometric drawing paper requires practice to master its use effectively:
- Start With Simple Shapes: Begin your practice by drawing basic shapes (e.g., cubes, pyramids) to familiarize yourself with the grid. This foundational work will build confidence as you progress to more complex designs.
- Combine Elements: Once you’re comfortable with basic shapes, experiment by combining them into more complex structures. For example, building intricate architecture or elaborate game level designs can be a fun practice exercise.
Care and Storage for Isometric Drawing Paper
1. Protecting Your Materials
To maintain the quality of isometric drawing paper, proper care is essential:
- Keep It Dry: Avoid exposing your paper to moisture, which can lead to warping or mildew. Store it in a cool, dry environment.
- Use Protective Covers: When transporting or storing your drawings, consider using protective covers or folders to prevent creases or tears.
2. Organizing Your Workspace
A tidy workspace boosts creativity:
- Designate a Drawing Area: Create a comfortable and organized area with all of your necessary supplies easily accessible.
- Categorizing Supplies: Organize tools and materials in a manner that makes them easy to find. Consider using storage containers or drawers to streamline your creative process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is grid paper called?
Grid paper is commonly referred to as “graph paper.” However, isometric drawing paper specifically features a triangular grid to facilitate three-dimensional representation.
What are the materials used in isometric drawing?
Typical materials used in isometric drawing may include isometric drawing paper, colored pencils, ink pens, rulers, and compasses. Artists might also use markers or digital tools for enhanced creativity.
What is the use of isometric dot paper?
Isometric dot paper includes dots arranged in an isometric grid layout, allowing artists to create three-dimensional shapes while maintaining proportional accuracy more flexibly.
Conclusion: Maximize Creativity with Isometric Drawing Paper
In summary, isometric drawing paper serves as an essential tool for artists, designers, and anyone involved in technical drawing. Its unique grid allows for precise, visually appealing representations of three-dimensional objects, making it indispensable across various industries.
By understanding its benefits, uses, and techniques, you can effectively utilize isometric drawing paper in your work to produce stunning and accurate designs. Whether you’re just starting your artistic journey or looking to refine your skills, incorporating isometric drawing paper into your practice can unlock new dimensions of creativity. Embrace this powerful tool and take your artistic endeavors to the next level!